NodeJS and Templating
Introduction
NodeJS enables server-side programming using JavaScript, allowing full-stack web development with a single language. This unit introduces NodeJS, Express, HTTP handling, and server-side templating with HandleBars.
Overview
What is NodeJS?
- An open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment.
- Executes JavaScript code server-side.
- Uses event-driven, non-blocking I/O for scalability.
- Great for real-time applications (e.g., chat apps, APIs).
Why Use NodeJS?
- Can process HTTP requests.
- Dynamically generates HTML pages.
- Handles file operations (read, write, delete).
- Interacts with databases.
- Collects and processes HTML form data.
Communication Across the Stack
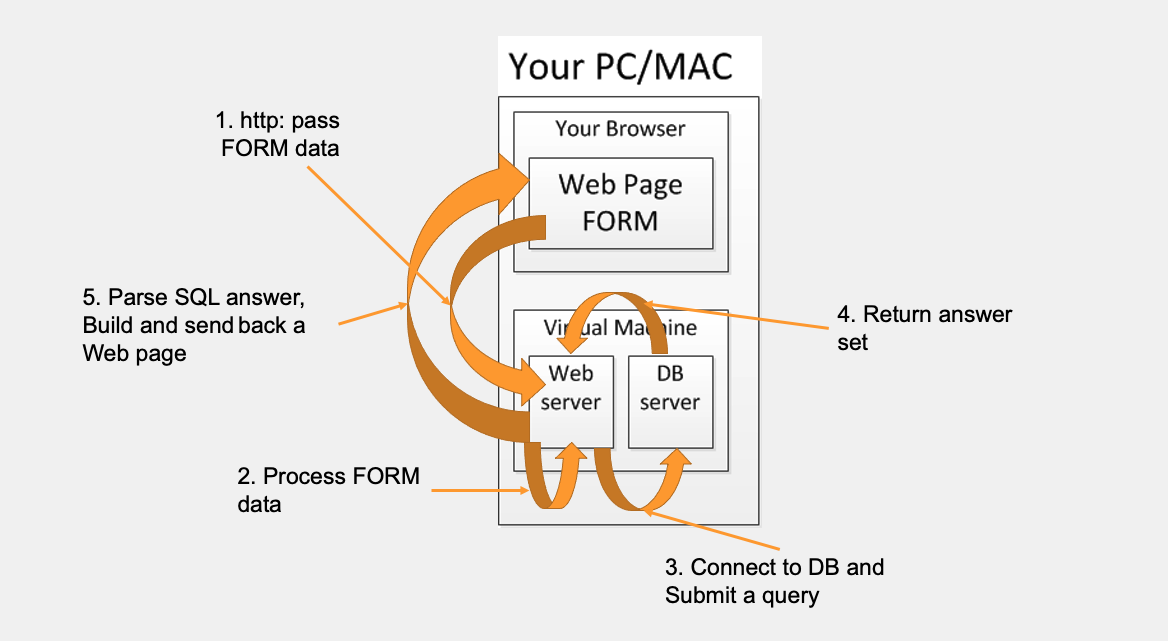
Express Framework
What is Express?
- Minimalist web framework for NodeJS.
- Simplifies routing, middleware handling, and response generation.
- Supports templates (e.g., EJS).
Basic Express App
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`);
});
Routing in Express
Routing defines how an application responds to client requests for specific endpoints (URLs) and HTTP methods.
Example:
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Home Page');
});
app.post('/addRecipe', (req, res) => {
res.send('Recipe added!');
});
Each route handles a specific URL and HTTP method (GET, POST, etc.).
Initializing a Node Project
Steps:
npm init→ Initializes a new project and createspackage.json.package.json→ Stores project metadata and dependencies.node_modules→ Folder containing installed packages..gitignore→ Excludesnode_modulesfrom version control.
Reading Client Input
GET Request (Query String)
app.get('/getRecipeById', (req, res) => {
let id = req.query.recipeId;
});
URL: localhost:<PORT>/getRecipeById?recipeId=1
GET Request (Route Parameter)
app.get('/getRecipeById/:recipeId', (req, res) => {
let id = req.params.recipeId;
});
URL: localhost:<PORT>/getRecipeById/1
POST Request (Body)
app.post('/addRecipe', (req, res) => {
let recipeName = req.body.recipeName;
let author = req.body.author;
});
- Data should not be sent in URL query for POST.
PUT Request (Body)
app.put('/updateRecipe', (req, res) => {
let recipeName = req.body.recipeName;
});
DELETE Request (Route Parameter)
app.delete('/deleteRecipe/:recipeName', (req, res) => {
let recipeName = req.params.recipeName;
});
Templating
What is Templating?
- Embeds dynamic data into HTML pages.
- Separates server logic from client-side UI.
- Improves scalability and maintainability.
Using Handlebars with Express
Installation
npm install express-handlebars
Setup in Express
const hbs = require('express-handlebars');
app.engine('handlebars', hbs.engine());
app.set('view engine', 'handlebars');
Handlebars Example
app.get('/recipe', (req, res) => {
res.render('recipe', {recipeName: 'Pasta', author: 'Chef John'});
});
In views/pages/recipe.hbs
<h1>{{recipeName}}</h1>
<p>By {{author}}</p>
Handlebars allows inserting server-side variables into HTML templates using double curly braces ({{ }}) for cleaner, logic-less templating.
Static Templates and Resources
Express can serve static files like images, CSS, and JS:
app.use(express.static('public'));
Files in the public/ directory are accessible to the client.
Best Practices
- Use
POSTfor sending sensitive data instead ofGET. - Validate user input before processing.
- Use
.gitignoreto avoid checking in node_modules. - Modularize routes and controllers for larger apps.
- Always sanitize user inputs to avoid security vulnerabilities.
Reflection Questions
- What is the difference between GET and POST requests?
- What is HandleBars used for?
- Why should
node_modulesbe included in.gitignore? - How do you send a parameter in a URL vs a body?
Summary
- NodeJS allows server-side scripting using JavaScript.
- Express simplifies the creation of web servers and routing.
- HandleBars templates enable dynamic HTML page rendering.
- Understanding HTTP methods and input handling is critical for full-stack development.
Disclaimer: Generative AI was used in part to generate these lecture notes.