Cloud Computing: Overview and Service Models
What Is Cloud Computing?
Imagine you've built a web app for your business or personal project. You want to make it available to the world and ensure that it can handle heavy traffic without crashing. One solution would be to buy and manage your own servers, but that can be expensive and time-consuming. Instead, you can use cloud computing to deploy your app using a global network of powerful computers managed by someone else.
Cloud computing lets you:
- Access computing resources over the internet
- Avoid managing physical servers
- Scale as needed and pay only for what you use
For example, companies use platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud to host their applications.

A Metaphor: The Electrical Grid
Think of cloud computing like electricity:
- You don’t know where it comes from
- It’s available when you need it—just plug in
- You use only what you need and pay accordingly
NIST Definition of Cloud Computing
“A model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.”
Pros of Cloud Computing
- Ubiquitous access – available from anywhere
- Scalable – increase or decrease resources easily
- Rapid deployment
- Lower costs
- Encourages innovation
- Uses modern architectures
Cons of Cloud Computing
- Less control over infrastructure
- Security risks (multi-tenancy, DDoS)
- Requires internet access
- Monitoring and compliance limitations
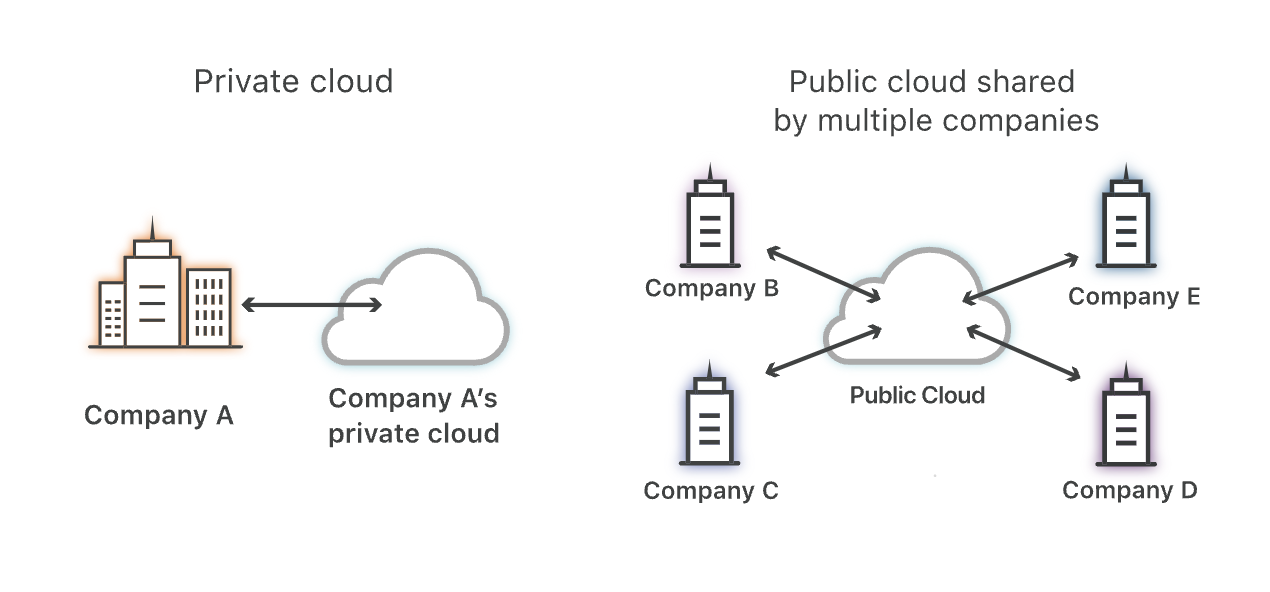
Public vs Private Clouds
Public Cloud
- Operated by third-party providers
- Shared by multiple customers
- Scalable and cost-effective
- Examples: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud
Private Cloud
- Exclusive to one organization
- More control, security, and customization
- Requires dedicated infrastructure
Cloud Service Models
Cloud services are offered in three main models:
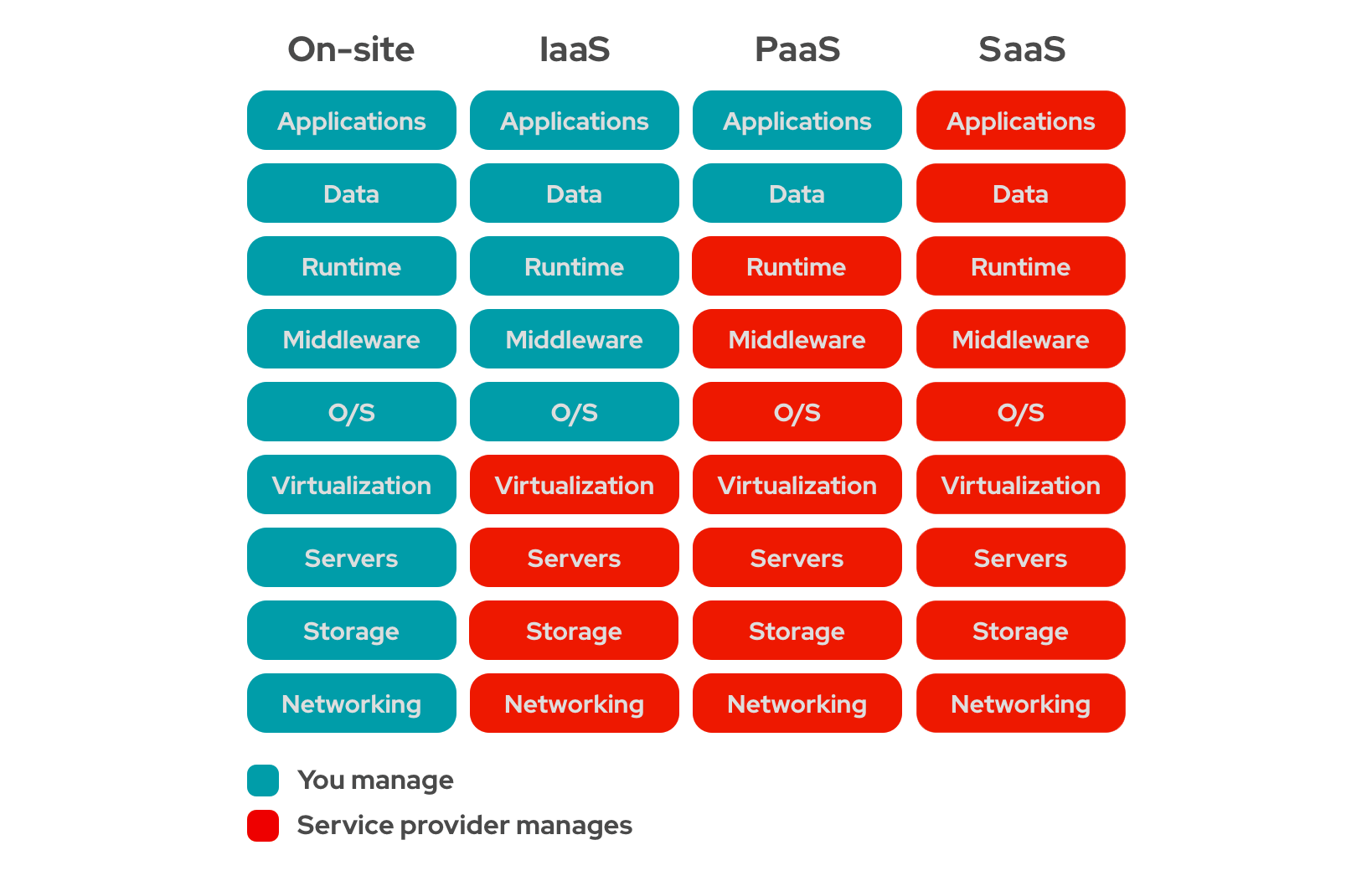
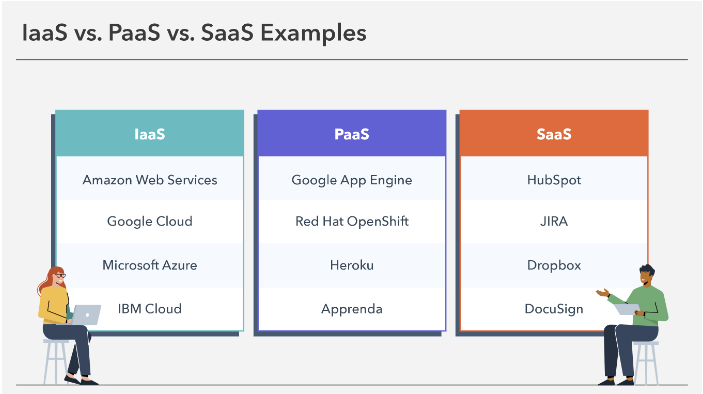
1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- Access to virtual servers, storage, and networks
- You manage the OS, middleware, and applications
- Example: AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure
Use Case: Hosting a web app on virtual machines with custom OS and configurations
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- Provides platforms and tools to develop applications
- You manage your code; the provider manages the environment
- Example: Heroku, Google App Engine
Use Case: Quickly build and deploy web apps without managing servers
3. SaaS (Software as a Service)
- Cloud-hosted applications accessed via browser
- Everything is managed by the provider
- Example: PayPal, Gmail, Zoom
Use Case: Subscribe to ready-made software without managing infrastructure
Who Manages What?
Each model offers a different level of control and responsibility.
Public and Private Clouds for IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
All three service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) can be deployed on both public and private clouds depending on the organization's needs.
- Public Cloud: Easy subscription to cloud services
- Private Cloud: Custom-built and managed internally
Popular Cloud Platforms
Some commonly used platforms include:
- AWS
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
Here's a great resource to explore more about cloud providers.
Reflection Questions
- What is the primary benefit of using cloud computing?
- What does “scalability” mean?
- Which of the following is not a type of cloud model?
Summary
- Cloud computing delivers resources on demand over the internet.
- It removes the burden of infrastructure management.
- Three main service models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
- Offered as public, private, or hybrid clouds
Disclaimer: Generative AI was used in part to generate these lecture notes.